Contents
Introduction
If you have an important VBA code base you know how difficult it is to maintain it, not because VBA is inherently a bad or poor platform but because the developers are often either end-users not aware of good development practices or professional developers not skilled enough in VBA development who have learnt it on the job. In both cases, more often than not, you end up with poor quality source code.
There is other forces that make VBA development less appealing, as the pressure of software vendors like Microsoft who’d like to sell you not just Office but Office+Visual Studio and then promotes other technologies like .Net with languages such as C# and VB.Net. Just have a look at the evolution of the VBA editor design and capabilities since 10 years and you’ll understand that it does not benefit from fanatic development and promotion efforts.
It’s why you should avoid the headlong rush and restrict your VBA development efforts to the bare minimum: for new developments you should consider other languages and platforms like C# and VB.Net with the .Net framework as they seamlessly integrate with the Office suite, with little overhead compared to the direct integration of VBA, and give you access to a wealth of modern technologies.
But don’t be fooled by the FUD about the dangers of keeping a legacy VBA code base and do your due diligence: does the guy who suggest you a full migration will do it for free or is he paid for the job? 😉 A full migration may be a necessity: not because the platform is VBA but because the application is buggy, undocumented, out of control and using it creates a true operational risk, and this is true for any application and technology including the newest.
Then, if you have a VBA application that is working perfectly, is documented and controlled, an alternative to both the headlong rush and the full migration is the integration of .Net components with VBA, you then use a future-proof technology to develop new features and/or replace legacy features as you go along, avoiding the big-bang effect.
So now you know what to do and right now I’ll show you how to do this seamless transition from VBA to greener pastures by implementing a simple API with three popular .Net languages: C# (the king), VB.Net (the prince) and C++/CLI (the Jack of all trades, master of none).
Presentation of the .Net API
The .Net API we’re going to build is a basic market-data provider that uses the Yahoo finance API as its back-end.
The API provides 4 methods:
- 3 unitary methods: GetBid, GetAsk, GetCapitalization, for retrieving the bid price, ask price and the capitalization of a stock, respectively,
- a bulk method: GetValues, for retrieving any set of fields (check this list of available fields to have an idea of which data you can get).
The code is minimal, with no error handling, to avoid any distraction.
We’ll write usual C#,VB.Net and C++/CLI code with some COM stuff: the Guid attribute to uniquely identify our COM-visible types and the ClassInterface attribute to control the way the COM interface is generated: “None” means we use the first interface explicitly implemented by the class.
If you don’t want to write any code or command-lines you can download this ZIP archive where I’ve packaged: the source-codes, a CMD script that builds and registers the API, and a demo Excel spreadsheet with VBA code (in the “mYahoo” VBA module).
You should just have to run the CMD script with administrator privileges from a Visual Studio Command Prompt, open the sample spreadsheet and click the “Load“ button.
The C# implementation
When it comes to selecting a language for .Net development C# is the default choice if you have no constraints because it was designed and is promoted as the flagship of the .Net framework. As such it benefits from a great development effort and a huge community.
Here is the C# implementation of our API:
using System.Net; // WebClient
using System.Runtime.InteropServices; // Guid, ClassInterface, ClassInterfaceType
using System.Globalization; // CultureInfo
[Guid("97E1D9DB-8478-4E56-9D6D-26D8EF13B100")]
public interface IYahooAPICS
{
double GetBid(string symbol);
double GetAsk(string symbol);
string GetCapitalization(string symbol);
string[] GetValues(string symbol, string fields);
}
[Guid("BBF87E31-77E2-46B6-8093-1689A144BFC6")]
[ClassInterface(ClassInterfaceType.None)]
public class YahooAPICS : IYahooAPICS
{
private static readonly WebClient webClient = new WebClient();
private const string UrlTemplate = "http://finance.yahoo.com/d/quotes.csv?s={0}&f={1}";
private static double ParseDouble(string value)
{
return double.Parse(value.Trim(), CultureInfo.InvariantCulture);
}
private static string[] GetDataFromYahoo(string symbol, string fields)
{
string request = string.Format(UrlTemplate, symbol, fields);
string rawData = webClient.DownloadString(request).Trim();
return rawData.Split(',');
}
public double GetBid(string symbol)
{
return ParseDouble(GetDataFromYahoo(symbol, "b3")[0]);
}
public double GetAsk(string symbol)
{
return ParseDouble(GetDataFromYahoo(symbol, "b2")[0]);
}
public string GetCapitalization(string symbol)
{
return GetDataFromYahoo(symbol, "j1")[0];
}
public string[] GetValues(string symbol, string fields)
{
return GetDataFromYahoo(symbol, fields);
}
}
We compile it using the CSC C# compiler:
csc /target:library FinanceCS.cs
Microsoft (R) Visual C# Compiler version 4.0.30319.17929
for Microsoft (R) .NET Framework 4.5
Copyright (C) Microsoft Corporation. All rights reserved.
“/target:library” asks CSC to generate a DLL rather than an EXE.
So we now have a “FinanceCS.dll” .Net DLL assembly.
The VB.Net implementation
In the .Net world VB.Net is your second choice if for any reason you have discarded C#. VB.Net is easier to grasp for VBA developers and can be an intermediate step on the road to full .Net applications: you won’t be distracted by a new language syntax and can concentrate on the .Net framework itself to get your productivity back quicker.
And this is what our API looks like in VB.Net:
imports System.Net ' WebClient
imports System.Runtime.InteropServices ' Guid, ClassInterface, ClassInterfaceType
imports System.Globalization ' CultureInfo
<Guid("FC06752C-C091-402F-A902-80D3D58DC861")>
Public Interface IYahooAPIVBNet
Function GetBid(symbol As String) As Double
Function GetAsk(symbol As String) As Double
Function GetCapitalization(symbol As String) As String
Function GetValues(symbol As String, fields As String) As String()
End Interface
<Guid("4103B22F-5424-46D6-A960-3C1440D96316")>
<ClassInterface(ClassInterfaceType.None)>
Public Class YahooAPIVBNet
Implements IYahooAPIVBNet
Private Shared ReadOnly webClient As WebClient = new WebClient()
Private Const UrlTemplate As String = "http://finance.yahoo.com/d/quotes.csv?s={0}&amp;amp;f={1}"
Private Shared Function ParseDouble(value As String) As Double
return Double.Parse(value.Trim(), CultureInfo.InvariantCulture)
End Function
Private Shared Function GetDataFromYahoo(symbol As String, fields As String) As String()
Dim request As String = String.Format(UrlTemplate, symbol, fields)
Dim rawData As String = webClient.DownloadString(request).Trim
return rawData.Split(New [Char]() {","})
End Function
Public Function GetBid(symbol As String) As Double Implements IYahooAPIVBNet.GetBid
return ParseDouble(GetDataFromYahoo(symbol, "b3")(0))
End Function
Public Function GetAsk(symbol As String) As Double Implements IYahooAPIVBNet.GetAsk
return ParseDouble(GetDataFromYahoo(Symbol, "b2")(0))
End Function
Public Function GetCapitalization(symbol As String) As String Implements IYahooAPIVBNet.GetCapitalization
return GetDataFromYahoo(symbol, "j1")(0)
End Function
Public Function GetValues(symbol As String, fields As String) As String() Implements IYahooAPIVBNet.GetValues
return GetDataFromYahoo(symbol, fields)
End Function
End Class
As with C#, compilation is straightforward, this time using the VBC VB.Net compiler:
vbc /target:library FinanceVBNet.vb
Microsoft (R) Visual Basic Compiler version 11.0.50709.17929
Copyright (c) Microsoft Corporation. All rights reserved.
As you’ve guessed “/target:library” has the same meaning for VBC and CSC: generating a DLL assembly rather then an EXE assembly.
And we get a “FinanceVBNet.dll” DLL.
The C++/CLI implementation
Why do I nickname C++/CLI the “Jack of all trades, master of none“?
“Jack of all trades” because it has the unique ability to talk to and be used by both native and managed components. It (almost) seamlessly mixes the two worlds in one place, what makes me consider C++/CLI as one of the most brilliant piece of software I’ve ever seen.
“Master of none” because C++/CLI is not your best choice for either .Net or native development:
- if you have no particular constraints and want a powerful language that integrates seamlessly with all the managed technologies (e.g. WPF) then your obvious choice is C#
- if you need high performance then you’ll go the native C++ way for your critical numerical code and let C# do the soft job
So, nowadays, C++/CLI is mainly pertinent as a great integration layer between the native and managed worlds (typically between C/C++ and C#): you’ll use it to build dumb wrappers, the plumbing that fills the gap between these two worlds.
I’ve decided to use C++/CLI here for educational purposes:
- first this is the rare occasion to put side by side C#, VB.Net and C++/CLI codes, which should hopefully helps those who use one or two of these languages and want to discover another one,
- second, for those who had the occasion to develop Excel extensions with native C++, it will demonstrate how easy it is now to build them with C++/CLI,
- third it will illustrate how the use of a common platform, .Net, will make the 3 seemingly different versions of the API deployable and usable in a single manner.
So here is the C++/CLI creature:
#using
using namespace System; // String
using namespace System::Net; // WebClient
using namespace System::Runtime::InteropServices; // Guid, ClassInterface, ClassInterfaceType
using namespace System::Globalization; // CultureInfo
[Guid("4ABC0C71-9CF5-4618-8D7C-55E32DCF6314")]
public interface class IYahooAPICPP
{
double GetBid(String^ symbol);
double GetAsk(String^ symbol);
String^ GetCapitalization(String^ symbol);
cli::array&amp;lt;String^&amp;gt;^ GetValues(String^ symbol, String^ fields);
};
[Guid("AEC520AE-12D8-49A9-A5F4-853112C3B6AD")]
[ClassInterface(ClassInterfaceType::None)]
public ref class YahooAPICPP : IYahooAPICPP
{
private: static initonly WebClient^ webClient = gcnew WebClient();
private: literal String^ UrlTemplate = "http://finance.yahoo.com/d/quotes.csv?s={0}&amp;amp;f={1}";
private: static double ParseDouble(String^ s)
{
return double::Parse(s-&amp;gt;Trim(), CultureInfo::InvariantCulture);
}
private: static cli::array&amp;lt;String^&amp;gt;^ GetDataFromYahoo(String^ symbol, String^ fields)
{
String^ request = String::Format(UrlTemplate, symbol, fields);
String^ rawData = webClient-&amp;gt;DownloadString(request)-&amp;gt;Trim();
return rawData-&amp;gt;Split(',');
}
public: virtual double GetBid(String^ symbol)
{
return ParseDouble(GetDataFromYahoo(symbol, "b3")[0]);
}
public: virtual double GetAsk(String^ symbol)
{
return ParseDouble(GetDataFromYahoo(symbol, "b2")[0]);
}
public: virtual String^ GetCapitalization(String^ symbol)
{
return GetDataFromYahoo(symbol, "j1")[0];
}
public: virtual cli::array&amp;lt;String^&amp;gt;^ GetValues(String^ symbol, String^ fields)
{
return GetDataFromYahoo(symbol, fields);
}
};
Not too frightening, except some oddities like these “^” everywhere and the magic “cli” namespace.
We compile it using the CL C++ compiler:
cl /clr:safe /LD FinanceCPP.cpp
Microsoft (R) C/C++ Optimizing Compiler Version 16.00.40219.01
for Microsoft (R) .NET Framework version 4.00.30319.18034
Copyright (C) Microsoft Corporation. All rights reserved.
FinanceCPP.cpp
Microsoft (R) Incremental Linker Version 10.00.40219.01
Copyright (C) Microsoft Corporation. All rights reserved.
/out:FinanceCPP.dll
/dll
/implib:FinanceCPP.lib
FinanceCPP.obj
“/clr:safe” is for generating a pure .Net assembly (by default CL generates native binaries while we want a CIL binary).
“/LD” asks CL to generate a DLL rather than an EXE.
This gives us our third DLL assembly: “FinanceCPP.dll“.
COM registration of the libraries
What is great with managed platforms like Java and .Net is that once you have your byte-code binaries you can use a single process to rule them all.
So here are the COM-registration commands for the 3 implementations of the API (you’ll need to run them with administrator privileges):
regasm /codebase /tlb FinanceCS.dll ... regasm /codebase /tlb FinanceVBNet.dll ... regasm /codebase /tlb FinanceCPP.dll ...
Some explanations:
- “/codebase” tells regasm to reference the assemblies full path into the registry, not only its name; otherwise your assembly should be put into the GAC which in this case is useless and would be pure overengineering (but sometimes, for assemblies shared by many applications, the GAC can be useful)
- “/tlb” tells regasm to generate and register a TLB file for the DLLs: a TLB file holds some metadata that will be consumed by the clients of our API to allow for a more user-friendly usage especially by allowing auto-completion in the VBA editor.
And if you try you’ll obtain this error:
RegAsm : error RA0000 : Could not load file or assembly 'file:///Z:\My\Path\On\The\Network\FinanceCS.dll' or one of its dependencies. Operation is not supported. (Exception from HRESULT: 0x80131515)
Here is another post that explains how you can change RegAsm configuration to make it accept loading from the network.
Note that in a production context you should not have this issue because you typically first install the DLL on the local drive, e.g. in “C:\Program Files\My Company\Finance Extensions\“, and then register it from there.
Our API is now ready to get used by VBA.
With Visual Studio
Compiling and registering by hand is the best way to understand what is going on under the hood, but in a production environment you’ll probably use Visual Studio to edit your code, compile it, and register the DLLs.
You must configure 2 things in Visual Studio to get the same behavior:
- Make the .NET assembly COM visible so that the classes you create will be registered into the Windows registry: go to the library project’s properties, then the “Application” tab, then click “Assembly Information“, and finally check “Make assembly COM-Visible“.
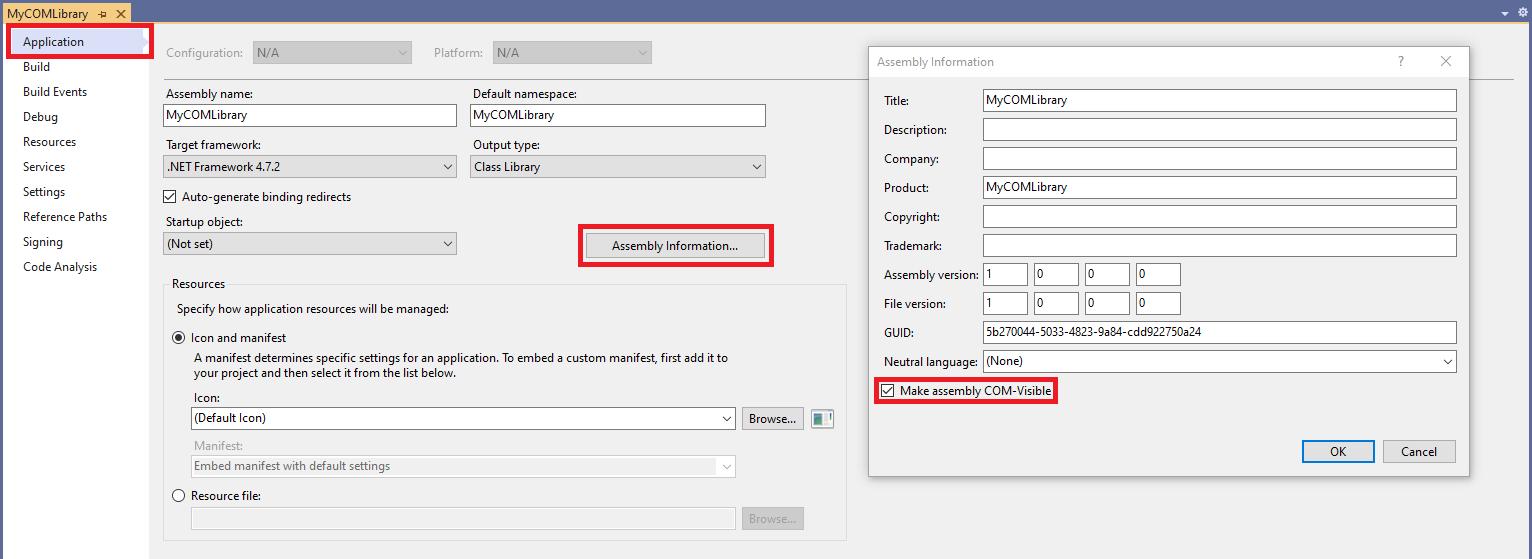
Make assembly COM visible - Register for COM interop: still in project’s properties go to the “Build” tab, then check “Register for COM interop“.
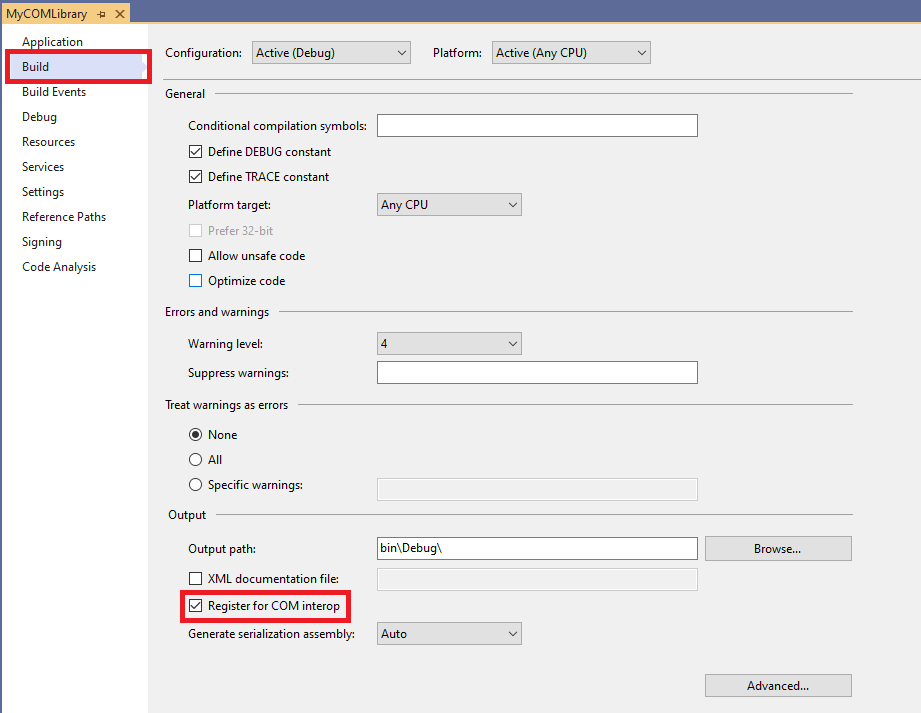
Register for COM interop
Using the API
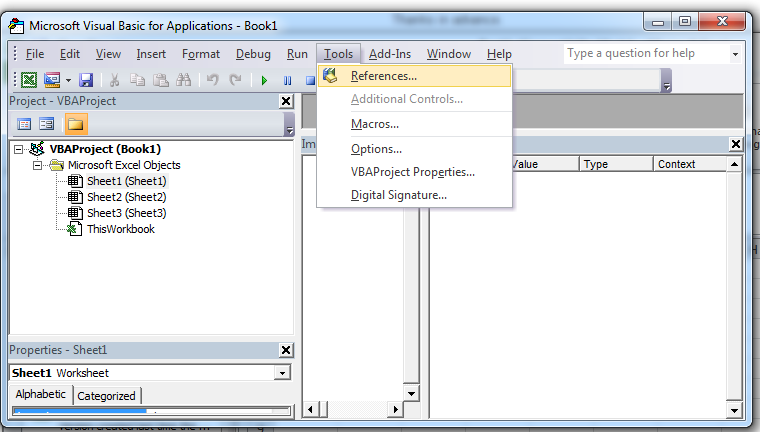
The first thing we need to do is referencing our 3 libraries TLBs:
go to the Excel VBA editor (shortcut: ALT-F11) and open the “References“ popup:
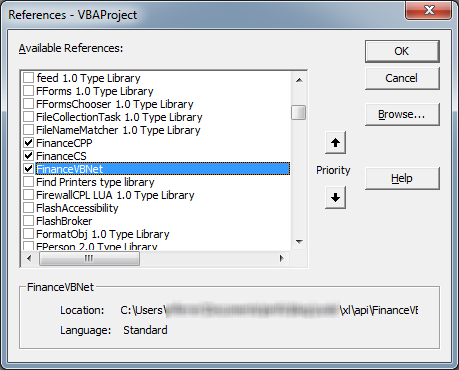
Then locate and select the “FinanceCS“, “FinanceVBNet” and “FinanceCPP” references:
You can now transparently use our YahooAPICS, YahooAPIVBNet and YahooAPICPP classes as if they were native VBA types.
Here is a basic example that retrieves and displays the bid price of Google using the C# implementation of the API:
Dim yahooAPI As New YahooAPICS
Call MsgBox("Google bid is: " &amp;amp; yahooAPI.GetBid("GOOG"))
(message for pedantic geeks: yes I know that As New is evil but I couldn’t resist ;))
Note: first call can be quite slow if you use IE automatic settings detection, so if you don’t need this feature disable it (see this thread for instructions).
Here is a more complete sample that you’ll find in the example spreadsheet in the “mYahoo“ VBA module:
Sub loadDataFromCS(output As Range)
Dim yahoo As FinanceCS.YahooAPICS
Set yahoo = New FinanceCS.YahooAPICS
output.Cells(1, 1).Value2 = yahoo.GetBid("GOOG")
output.Cells(1, 2).Value2 = yahoo.GetAsk("GOOG")
output.Cells(1, 3).Value2 = yahoo.GetCapitalization("GOOG")
Dim bidAskCapi As Variant
bidAskCapi = yahoo.GetValues("GOOG", "b3b2j1")
output.Cells(1, 4) = bidAskCapi(0)
output.Cells(1, 5) = bidAskCapi(1)
output.Cells(1, 6) = bidAskCapi(2)
End Sub
Sub loadDataFromVBNet(output As Range)
Dim yahoo As FinanceVBNet.YahooAPIVBNet
Set yahoo = New FinanceVBNet.YahooAPIVBNet
output.Cells(1, 1).Value2 = yahoo.GetBid("GOOG")
output.Cells(1, 2).Value2 = yahoo.GetAsk("GOOG")
output.Cells(1, 3).Value2 = yahoo.GetCapitalization("GOOG")
Dim bidAskCapi As Variant
bidAskCapi = yahoo.GetValues("GOOG", "b3b2j1")
output.Cells(1, 4) = bidAskCapi(0)
output.Cells(1, 5) = bidAskCapi(1)
output.Cells(1, 6) = bidAskCapi(2)
End Sub
Sub loadDataFromCPPCLI(output As Range)
Dim yahoo As FinanceCPP.YahooAPICPP
Set yahoo = New FinanceCPP.YahooAPICPP
output.Cells(1, 1).Value2 = yahoo.GetBid("GOOG")
output.Cells(1, 2).Value2 = yahoo.GetAsk("GOOG")
output.Cells(1, 3).Value2 = yahoo.GetCapitalization("GOOG")
Dim bidAskCapi As Variant
bidAskCapi = yahoo.GetValues("GOOG", "b3b2j1")
output.Cells(1, 4) = bidAskCapi(0)
output.Cells(1, 5) = bidAskCapi(1)
output.Cells(1, 6) = bidAskCapi(2)
End Sub
Sub GetDataButton_Click()
Dim dataSheet As Worksheet
Set dataSheet = Sheets("Data")
dataSheet.Range("B2").Resize(3, 6).ClearContents
Call loadDataFromCS(dataSheet.Range("B2"))
Call loadDataFromVBNet(dataSheet.Range("B3"))
Call loadDataFromCPPCLI(dataSheet.Range("B4"))
dataSheet.Cells.Columns.AutoFit
dataSheet.Cells.Rows.AutoFit
End Sub
As you see, whatever the language used, the objects declaration, instantiation and usage are strictly the same, you just use different classes: YahooAPICS, YahooAPIVBNet and YahooAPICPP.
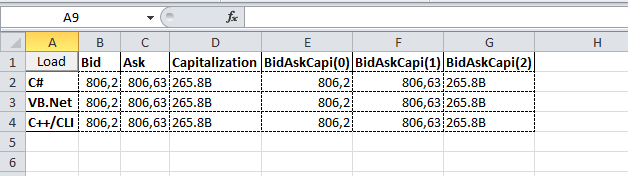
Demo
Here is what you get when using the demo spreadsheet included into the archive attached with this article:
Conclusion
I hope this article has helped you realize that interfacing VBA and .Net is a relatively straightforward process: implement with the language you want, compile, register and enjoy!
But this is not all rosy with COM interop because as a universal layer of abstraction between different technologies it had to choose a common denominator, so there is features in .Net you can’t use with COM interop like non default constructors, methods overloading or static methods.
All these limitations are not critical and can be easily workaround keeping quality to a high level; you can check this article if you want more details on the design decisions you may have to take with .Net/VBA COM interop: How I Came to Love COM Interoperability.
Of course there is more to .Net development than this, but adding additional features like error-handling, logging, or graphical user interfaces, is much more convenient within the .Net environment (especially with Visual Studio which is a great IDE) than it is in the more limited world of VBA.
If you have any question, issue or suggestion please feel free to let a comment, I’ll do my best to answer it in a timely fashion.
Your post was very informative thank you for that
Very useful article. I do everything as described and everything works. but when I reran Access I have error: Module not found.The problem goes away when I reconnect the Reference.Do You not know how to solve this problem?
Thanks for the feedback Nik.
Do you save the Access project after referencing?
Have you the same issue with Excel?
I have been using VBA for 7 years in my Excel Models. I have no coding experience beyond VBA. My consultant tells me I have far exceeded the intended use of VBA in driving Excel. He says it is time to move to .net etc.
I have no clue where to start. I have all the MicroSoft .net loaded on my computer but no clue how to get to first base.
Suggestions?
Hello Richard,
you should use Visual Studio, it will be far easier to create your COM components.
I’ve added a section on how to configure COM interop in VS projects.
As for the language, VB.NET is, of course, closer to VBA, but in the .NET ecosystem the king is C#, so I highly advise you to learn it.
At first sight it can be impressive with all these braces, semi-colons, and new keywords, but you’ll quickly become fluent with it as the building blocks are the same as in any language: functions, conditions, loops…
Moreover, whatever the language you’ll use, .NET is fully object-oriented so you’ll have to write classes, so OOP is another important feature to learn.